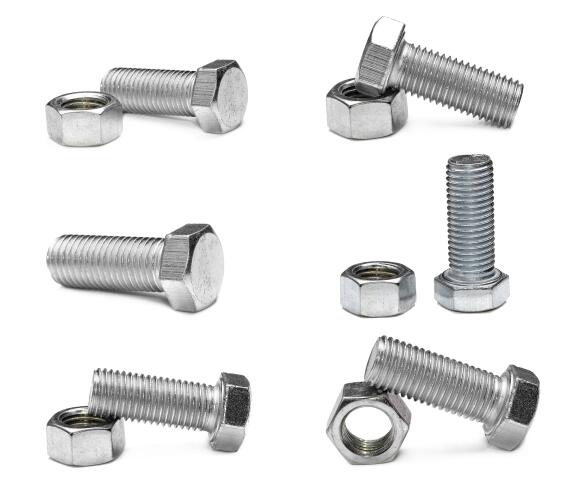
Prince Fastener:The difference between bolts and screws
Bolts, screws, and nuts are often mentioned in daily life, so what is the difference between them? There is no standard term for screws and nuts. The screw is the common name, with external threads can be called “screws.” The nut is the common name; the standard should be called “nut.” the shape of the nut is usually hexagonal; the inner hole for the internal thread, used with the bolt, tightens the relevant parts. The head of the bolt is usually hexagonal, with external threads on the rod. Screws are smaller, with a flat head, crosshead, etc., and a rod with external threads. Studs should be called “double-headed studs,” both ends have external threads, and the middle is usually a bare rod. The long end of the thread connects to the deep hole, and the short section is connected to the nut.
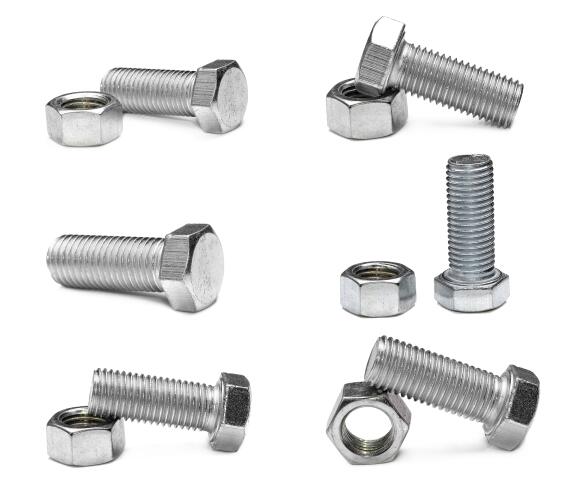

Bolts and screws are standard fasteners used in various fields and equipment, mainly to connect and fix. Prince Fastener today will share the differences between bolts and screws and hope that they will be helpful to you in the future.
Standard fasteners are divided into thirteen categories: the selection of fasteners according to the occasion’s use and its function to determine.
Bolts and screws are different:
1, Bbolts and screws are defined differently:
Bolts: bolts are used in pairing with nuts to use cylindrical fasteners with threads. Mainly used to fasten the connection of two parts through holes, this form becomes a bolt connection.
Screws, also known as screws, use the physical and mathematical principles of beveled circular rotation and friction to tighten objects and machines circularly and progressively. Its fastening screw is used to fix the relative position of the machine parts. Screw the set screw into the screw hole of the part to be fastened, to its end pressed on the surface of another part; that is, the former part is fixed on the latter part.
2, Bolt and screw shape structure is different:
Bolt: by the head and screw (with the external thread of the cylinder), two parts of a class of fasteners, the head is primarily hexagonal head, etc., generally larger.
Screw: a class of fasteners consisting of two parts: the head and screw, the head is mostly a slot, cross slot, the internal and external hexagon is also a lot, generally smaller.
3, Bolt and screw applications are different:
Bolts: generally used in pairs with nuts for through-holes, easily replaced after damage.
Screws: usually do not need nuts, directly with two objects (generally connected first to drill holes, tapping threads) more for blind holes; the corresponding parts are rarely disassembled.
4, Bolt and screw using for different tools:
Bolts generally use wrench-type tools.
Screws generally use a driver-type tool.
5, Bolts and screws fastening different:
Bolts are generally used with nuts or screwed into the processed bolt holes.
Screws, in addition to the two fastening methods of bolts and self-tapping screws, are directly screwed into the workpiece of soft materials, without processing bolt holes, such as what we call wood screws is this screw.
6, Bolts and screws are used on different occasions:
Bolts and screws are used in different places; bolts do not require high precision unless there are requirements with the available bolt easy to disassemble, low processing accuracy, not subject to coupling material restrictions, widely used, with the requirements of the bolt, can withstand lateral loads;
Screws in the structure of compact, but can not often disassemble, and can not withstand immense forces.

① Bolts
a) General purpose bolts: There are many varieties, including hexagonal head and square head. Hexagon head bolts are most commonly used and are divided into A, B, C, and other product grades according to manufacturing accuracy and product quality, with A and B grade being the most used, and are mainly used for important, high assembly accuracy and where they are subject to large shocks, vibrations or variable loads. Hexagon head bolts can be divided into two types of hexagonal head and large hexagonal head according to the size of the head support area and the size of the installation position; the varieties with holes in the head or screw are used when locking is required. Squarehead bolts have a larger size and force surface, which is convenient for the wrench mouth to catch or lean on other parts to stop the role of rotation, commonly used in rougher structures, sometimes also used in T-slots, to facilitate the bolt in the slot to adjust the position of the loosening. See GB8, GB5780 ~ 5790, etc.
b) Reamed holes with bolts: the use of bolts closely set into the reamed hole to prevent the workpiece misalignment, see GB27, etc.
c) Stop bolt: square neck, with tenon, see GB12 ~ 15, etc.
d) Special purpose bolts: T-slot bolts, live bolts, and foot bolts. T-slot bolts are mostly used in places that need to be disconnected frequently; foot bolts are used in cement foundations to fix the rack or motor base. See GB798, GB799, etc..
e) Steel structure with high-strength bolts to connect the vice: generally used in buildings, bridges, towers, pipe supports and lifting machinery, and other steel structures friction-type connection occasions, see GB3632, etc.
② Nuts
a) General-purpose nuts: many varieties, hexagonal nuts, square nuts, etc. According to manufacturing precision, hexagon nuts with hexagonal bolts are most commonly used, and product quality is divided into A, B, C grade, and other product grades. Hexagon thin nuts are used as sub-nuts in anti-loosening devices, playing a locking role, or for threaded connections where the vice is mainly subjected to shear forces. Hexagonal thick nuts are mostly used in the connection of frequent disassembly. Square nuts and square-headed bolts with a wrench stuck are not easy to slip, mostly used in a rough, simple structure. See GB41, GB6170~6177, etc..
b) Slotted nuts: mainly refers to hexagonal slotted nuts, i.e., the slot is machined above the hexagonal nut. It is used with the screw with holes in the bolt and cotter pin to prevent the bolt and nut relative rotation; see GB6178 ~ 6181 and so on.
c) Locknut: refers to the nut with locking function; nylon insert hexagonal lock nuts and all-metal hexagonal lock nuts, etc. Hexagonal nylon ring lock nuts have a very reliable anti-loosening ability, in the use of temperature -60 ~ +100 ℃ and certain medium conditions, with no damage to the bolt and the corresponding parts and can be frequently loaded and unloaded and other points. See GB889, GB6182~6187, etc.
d) Special purpose nuts: such as butterfly nuts, cover nuts, knurled nuts, embedded nuts, etc. Butterfly nuts can generally be disassembled without tools, usually used for frequent disassembly, and force is not much; cover nuts used at the end of the buckle need to cover the place. See GB62, GB63, GB802, GB923, GB806, GB807, GB809, etc.
③ Screws
a) Machine screws: divided into many varieties due to different head and slot shapes. The head type has a cylindrical head, pan head, countersunk head, and semi-countersunk head several, head slot shapes is a generally open slot (a slot), cross slot, and hexagonal slot three. Cross-slotted screws have good alignment when screwing; the head strength is greater than a word slot, not easy to screw bald, generally used in mass production of luxury furniture china. Hexagon socket screws, hexagon socket screws can be applied to a larger tightening torque, connection strength, the head can be buried in the body, for the requirements of the compact structure, smooth shape of the connection. See GB65, GB67-69 and GB818-820, etc..

b) Set screws: set screws for fixing the relative position of the parts, the head with a slot, hexagonal and square head, and other types. Squarehead can apply a larger tightening torque. The maximum tightening force is large, not easy to screw bald, but the head size is large, inconvenient, buried in the parts, not safe, especially the moving parts should not be used. With a slot, the hexagonal is easy to sink into the parts. Fastening screw end according to the use of different requirements, generally, the most commonly used cone end, flat end, cylindrical end three.
The tapered end is suitable for the small hardness of the parts; when using screws without a tip of the cone end, the top tightening surface of the parts to play pit eyes when the cone surface is pressed on the edge of the pit.
The end for the flat end of the screw, large contact area, top tightening does not hurt the surface of the parts, used for maximum tightening hardness of the plane or often adjust the position of the occasion.
The end of the cylindrical end of the screw does not damage the surface of the parts, mostly used to fix the parts mounted on the pipe shaft (thin-walled parts), the cylindrical end of the top into the hole on the shaft kind, by the round end of the shear resistance, can transmit a larger load. See GB71, GB73 to 75, GB77 to 78, etc..
c) Hexagon socket screws: hexagon socket screws are suitable for installation space is small, or the head of the screw needs to be buried; see GB70, GB6190 ~ 6191 and GB2672 ~ 2674, etc.
d) Special-purpose screws: positioning screws, screws and hanging ring screws do not come off, see GB72, GB828 ~ 829, GB837 ~ 839, GB948 ~ 949 and GB825, etc..
④ Studs
a) Unequal length double-headed stud: for one end screwed into the body of the part to connect or fasten the role of the occasion, see GB897 ~ 900.
b) Equal-length double-headed stud: applicable to both ends with the nut to connect or fixed distance role. See GB901, GB953, etc.
⑤ Wood screws
It is divided into many varieties due to different head and slot shapes. Head type has a round head, countersunk head, semi-countersunk head, etc. The head slot (a slot) crosses slot two; see GB99 ~ 101, GB950 ~ 952.
⑥ Self-tapping screws
a) Ordinary self-tapping screws: thread in line with GB5280, pitch large, suitable for use in thin steel or copper, aluminum, plastic, see GB845 ~ 847, GB5282 ~ 5284, etc.
b) Self-tapping locking screws: thread in line with the common metric coarse thread, suitable for use in the need for vibration-resistant occasions; see GB6560 ~ 6564.
(7) Washers
a) Flat washers: used to overcome the workpiece support surface is not flat and increase the support surface stress area, see GB848, GB95 ~ 97 and GB5287;
b) Spring (elastic) washers: spring washers rely on elasticity and beveled friction to prevent the loosening of fasteners, widely used for frequent disassembly of the connection. Inner tooth elastic washer, outer tooth elastic washer circumference with a lot of sharp elastic warp teeth, stabbing pressure on the support surface, can stop the fastener loosening. Inner tooth elastic washer for the head size of the smaller screw head; outer tooth elastic washer for the bolt head and nut. Elastic washer with teeth than ordinary spring washer volume is small, fasteners uniform force, prevent loosening is also reliable, but should not be used for often disassembled. See GB93, GB859 ~ 860 and GB955.
c) Stop washers: there are internal teeth locking washers, external teeth locking washers, single-ear stop washers, double-ear stop washers, round nuts with stop washers, and so on. Single-ear and double-ear stop washers allow the nut to tighten in any position to lock, but the fastener supplier needs to be appropriate against the edge, see GB861 ~ 862, GB854 ~ 855, GB858, etc.;
d) Oblique washers: To adapt to the slope of the work support surface, can use oblique washers. Square oblique washers are used to channel, I-beam flange, and other inclined surface pad flat so that the nut support surface perpendicular to the nail rod, to avoid tightening the nut so that the screw bending force. See GB852 ~ 853, etc.

⑧ Retaining ring
a) Elastic retaining ring: shaft and hole with elastic retaining ring card in the shaft groove or hole groove for rolling bearing installed after stopping with, in addition to the shaft with an open retaining ring, mainly used to the card in the shaft groove for parts positioning, but can not bear the axial force. See GB893 ~ 894 and GB896;
b) Wire retaining ring: there are holes (shaft) wire retaining ring and wire lock ring. Steel wire retaining ring installed in the shaft groove or hole groove for parts positioning can also withstand certain axial forces. See GB895.1 ~ .2, GB921.
c) Shaft parts with locking retaining ring: with a taper pin locking retaining ring and screw locking retaining ring, mainly used to prevent the axial movement of the shaft parts. See GB883 ~ 892.
d) shaft end retaining ring: the use of screw fastening shaft end retaining ring and bolt fastening shaft end retaining ring, mainly used to lock the parts fixed in the shaft end. See GB883 ~ 982.
⑨ Pin
a) Cylindrical pins: cylindrical pins are used to fix parts on the shaft, power transmission, or positioning elements. Cylindrical pins have different diameter tolerances can be used for different fit requirements. Cylindrical pins are generally fixed in the hole by interference, so it is not suitable for more disassembly. See GB119 ~ 120, GB878 ~ 880, etc..
b Taper pin: taper pin with a taper of 1:50, easy to install the right eye, but also to ensure self-locking, generally used as positioning elements and connecting elements, mostly used in places requiring frequent disassembly. Taper pins with internal thread and screw-tail taper pins are used in holes that are not pierced or in holes where it isn’t easy to drive pins. Open-ended taper pins can be opened after being punched into the hole to prevent the pin itself from slipping out of the hole. See GB117 ~ 118, GB881 and GB877, etc.
Cylindrical pin and a variety of tapered pinholes generally need to go through the reaming process; many times after the installation and removal will reduce the accuracy of positioning and connection tightness and can only transmit a small load. The elastic cylindrical pin itself has elasticity, installed in the hole to maintain tension, is not easy to loosen, easy to disassemble, and does not affect the nature of the fit; the pinhole does not need to be reamed—pins with holes and pins, both for reaming connections.
c)Cotter pin: cotter pin is connected to the machine parts of the anti-loosening device when used through the nuts, bolts with pinholes, or other connecting parts of the pinhole, and then the foot apart. See GB91.
⑩Rivet
a) Hot forging forming rivets: more extensive specifications, primarily used in locomotives, ships and boilers, etc., usually require hot forging to shape the head; see GB863 ~ 866.
b) Cold heading rivets: the general diameter specification 16mm, usually through cold heading so that the head molding, see GB867 ~ 870, GB109, etc.
c) Hollow and semi-hollow rivets: hollow rivets are used for shear force is not much, often used to connect plastic, leather, wood, canvas, and other non-metallic parts.